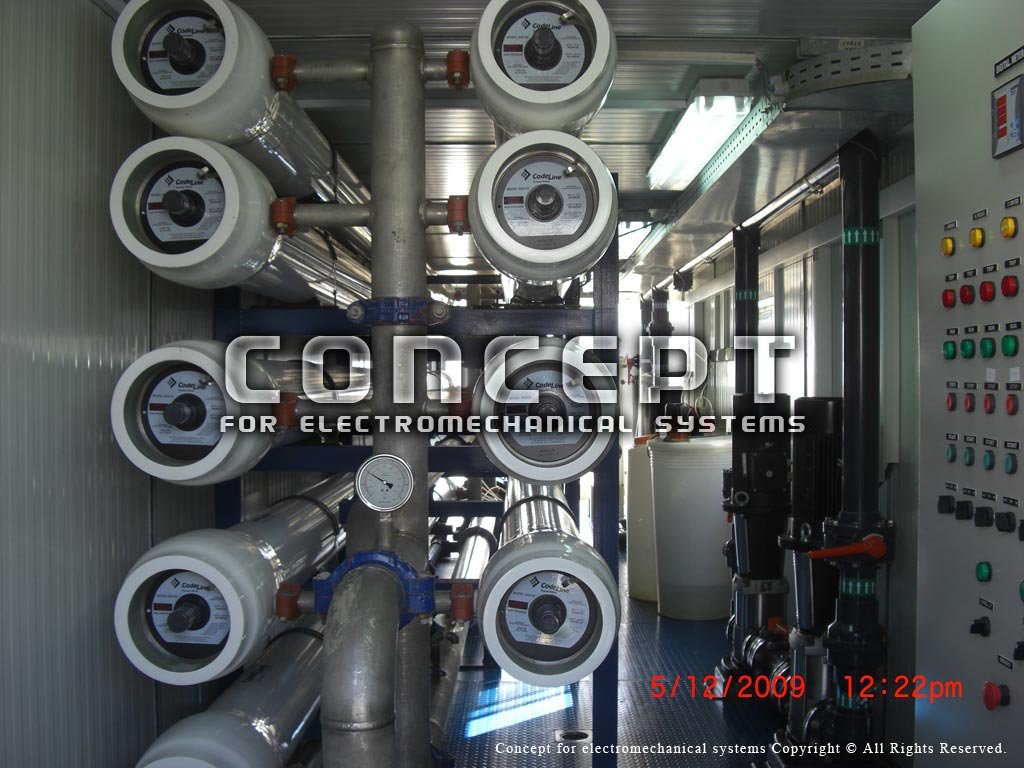
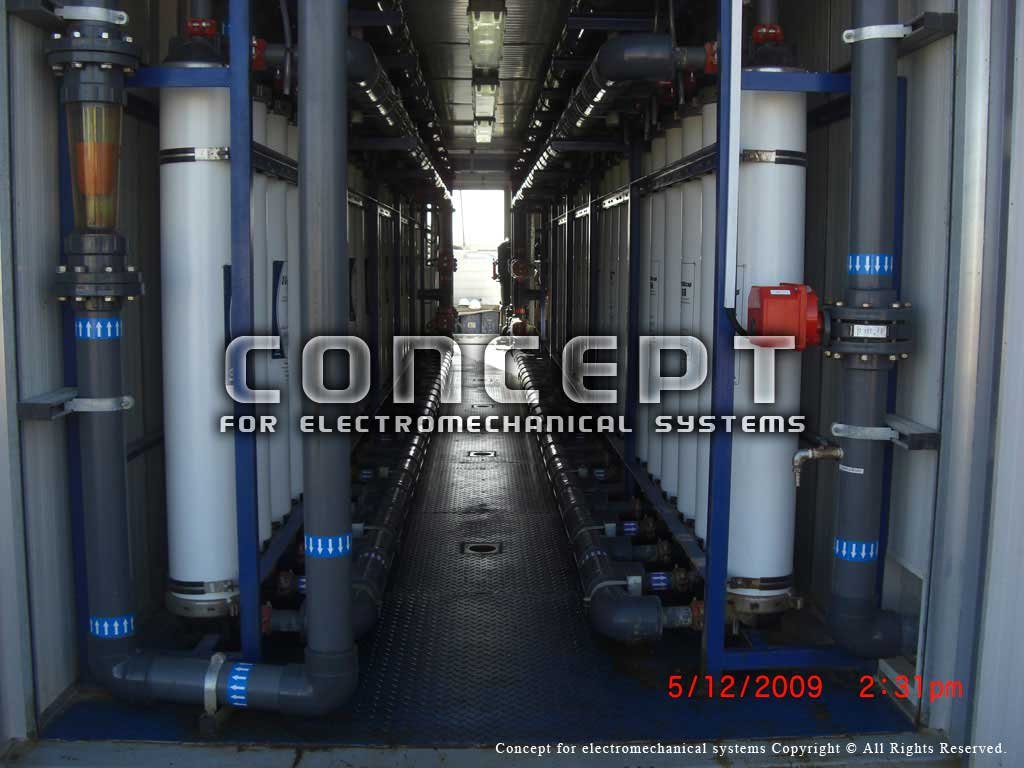
The reverse osmosis process produces one of the purest forms of water available - it is perfectly suitable for drinking, bottling or for use in industrial processes where high purity is necessary.
During reverse osmosis, dissolved solids, organics, colloidal matter, bacteria and viruses are removed from the water.
Reverse Osmosis (RO)is a membrane-technology filtration method that removes many types of large molecules and ions from solutions by applying pressure to the solution when it is on one side of a selective membrane. The result is that the solute is retained on the pressurized side of the membrane and the pure solvent is allowed to pass to the other side.
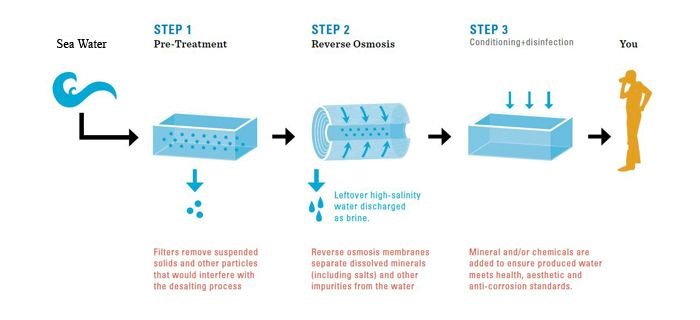
Reverse Osmosis process using thin-film composite membranes has evolved over the last 20 years and has brought down the cost of desalination. Major improvements in the membranes, energy recovery, pumps and pressure vessels have brought down the cost of desalinated water significantly.
There's two types of Reverse Osmosis (RO) units and the choice between them depends on the analysis of the water that needs to be desalinated
The different between the two units is in the type of membranes and Pressure values and the unit materials.


